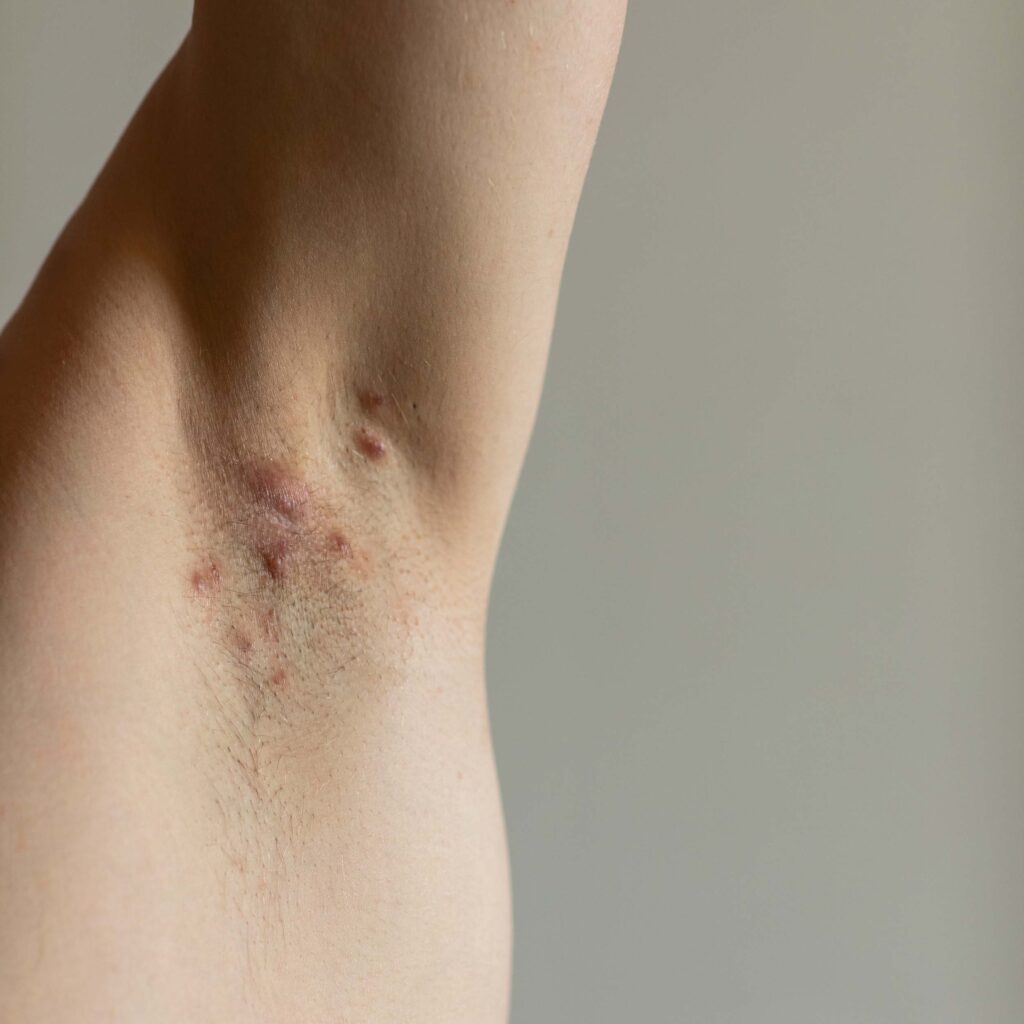
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic debilitating systemic skin disease which results in painful inflammation of the hair follicles, most notably in the armpit, groin and genital regions. The clinical hallmarks of this disease include very painful inflammatory nodules, boils or abscesses that typically open and release odorous inflammatory fluids. In the more chronic form of the disease, patients experience draining fistulas, also referred to as sinus tracts, which ultimately lead to scarring and related functional disability in certain areas. HS patients suffer primarily from pain and significant discomfort resulting from the constant formation of pus, often requiring the use of bandages and diapers, resulting in social isolation. Not surprisingly, HS is severely and adversely affects patients’ quality of life.
Source: Diagnosed patients incl. US and EU5 based on meta-analysis by Phan K., et al. (2020) and EvaluatePharma (2023 est.)
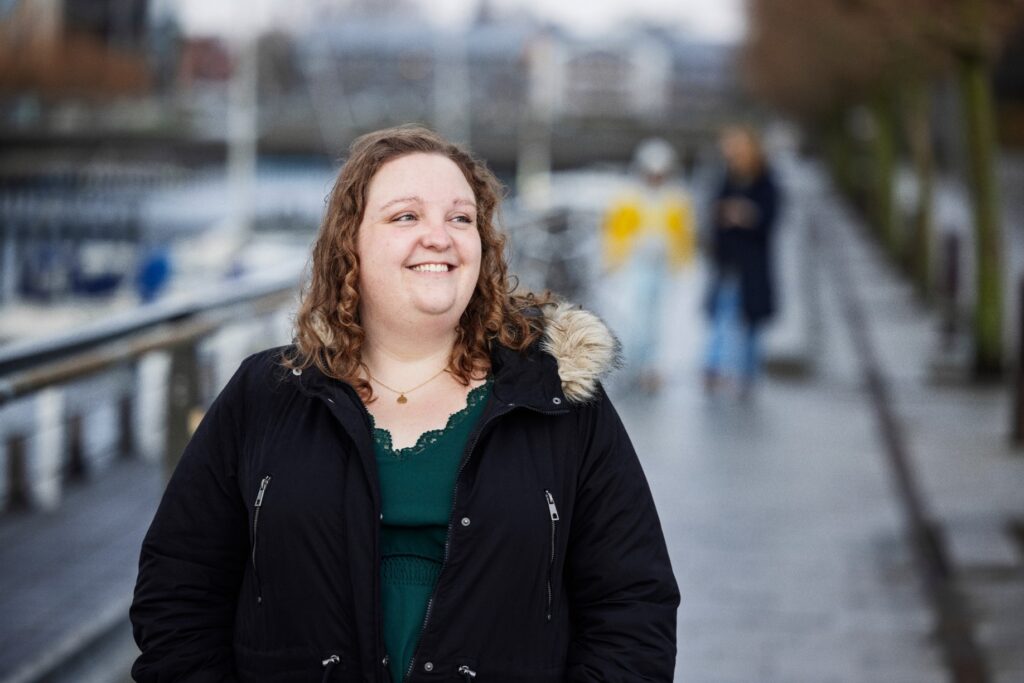
Meet Sara, a woman living with
Hidradenitis Suppurativa since the age of 15.
Read Sara’s story
Meet Janne, a woman and mother living with hidradenitis suppurativa.
Mild-to-Moderate
13,4M suffers from Psoriasis in the US, EU5 and Japan
PDE4 inhibitor
Dermatology market and include
topical roflumilast cream
PDE4 Market and include
topical roflumilast cream
Moderate-to-servere
People in the US suffer from Psoriasis
TNF-Q + 11-17
Plaque psoriasis and atopic
dermatitis
Acim quam ratem eos dis ma
doluptatist
Checkpoint-for Psoriasis
People in EU5 suffer from Psoriasis
Keratinoc
Exerting anti-inflammatory effect
reducing psoriasis scale formation
PDE4 Market and include
topical roflumilast cream
Treatment of HS
The diagnosis and treatment of HS is generally challenging due to limited awareness of the disease, resulting in the disease often being overlooked. In most countries, treatment is handled by dermatologists, even though many patients often seek advice from primary care physicians or even to emergency departments in order to get surgical relief of formed abscesses.
The general standard of care for HS patients includes topical, oral or intravenous antibiotic treatment which often provide only temporary symptomatic relief. In some cases, patients also undergo different types of surgery. HS is recognized as a systemic inflammatory disease, for which there are numerous suggested etiological factors, including genetics.
There is only one approved treatment available today for treatment of moderate to severe HS, which received orphan drug designation in 2015. There are no treatments approved for mild HS. Adjunctive therapies, off-label, include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (“NSAIDs”), antibiotics, corticosteroids, oral retinoids, topical resorcinol, and hormone therapy.
UNION is developing oral orismilast for the treatment of HS.
Read more about orismilast here.